Introduction:
Salt contamination is a critical factor that can adversely impact the performance and durability of coatings applied to surfaces, especially in industries such as marine, automotive, and infrastructure. Salt contamination can lead to coating adhesion failures, corrosion, and decreased longevity. The salt value, often referred to as the salt concentration or salt contamination level, indicates the amount of soluble salts present on a surface. In the context of blasted surfaces, which are prepared for coating applications, assessing the salt value is crucial to ensure proper adhesion and protection.


References:
This blog gathers information from industry standards such as ISO 8502-6, ASTM D4940, and NACE International standards. Information has also been drawn from reputable websites like the SSPC (The Society for Protective Coatings), coating manufacturers' technical resources, and published papers in corrosion and coating-related journals.
Stepwise Process:
Instrument Setup: Begin by setting up the necessary equipment, including a conductivity meter and appropriate testing solutions.
Blank Test: Perform a blank test by using the testing solution on a clean, uncontaminated surface. This establishes a baseline for conductivity readings.
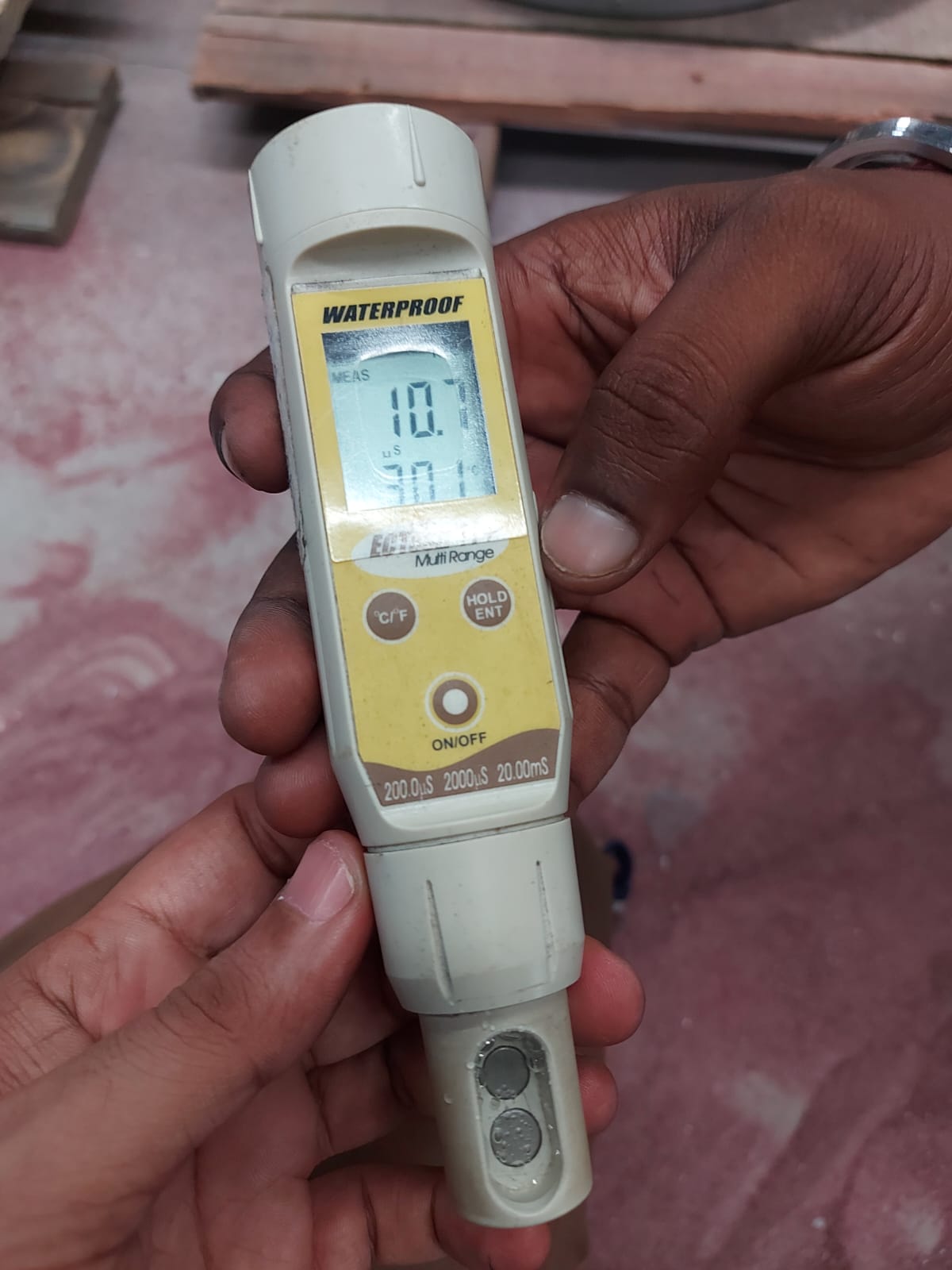
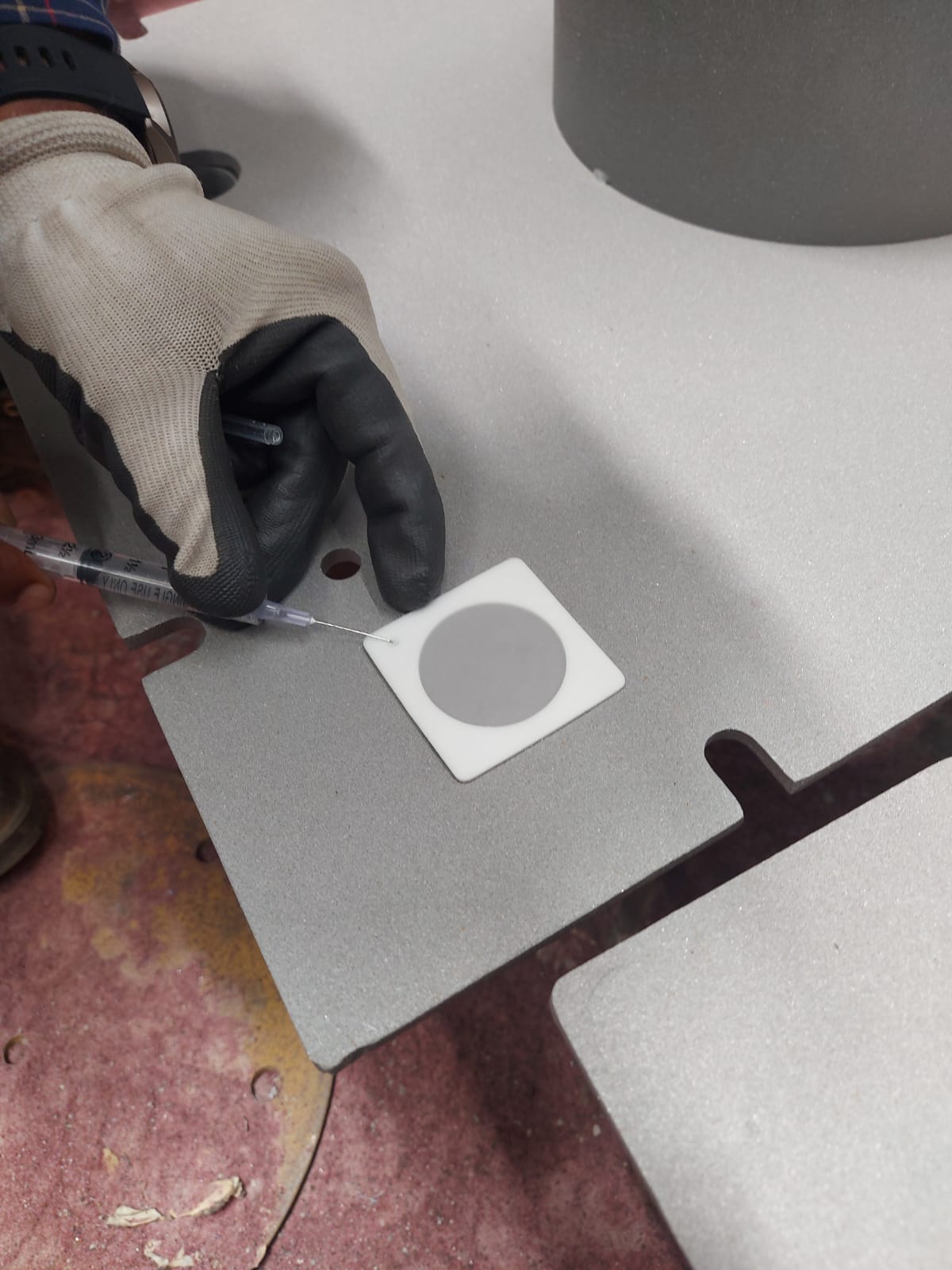
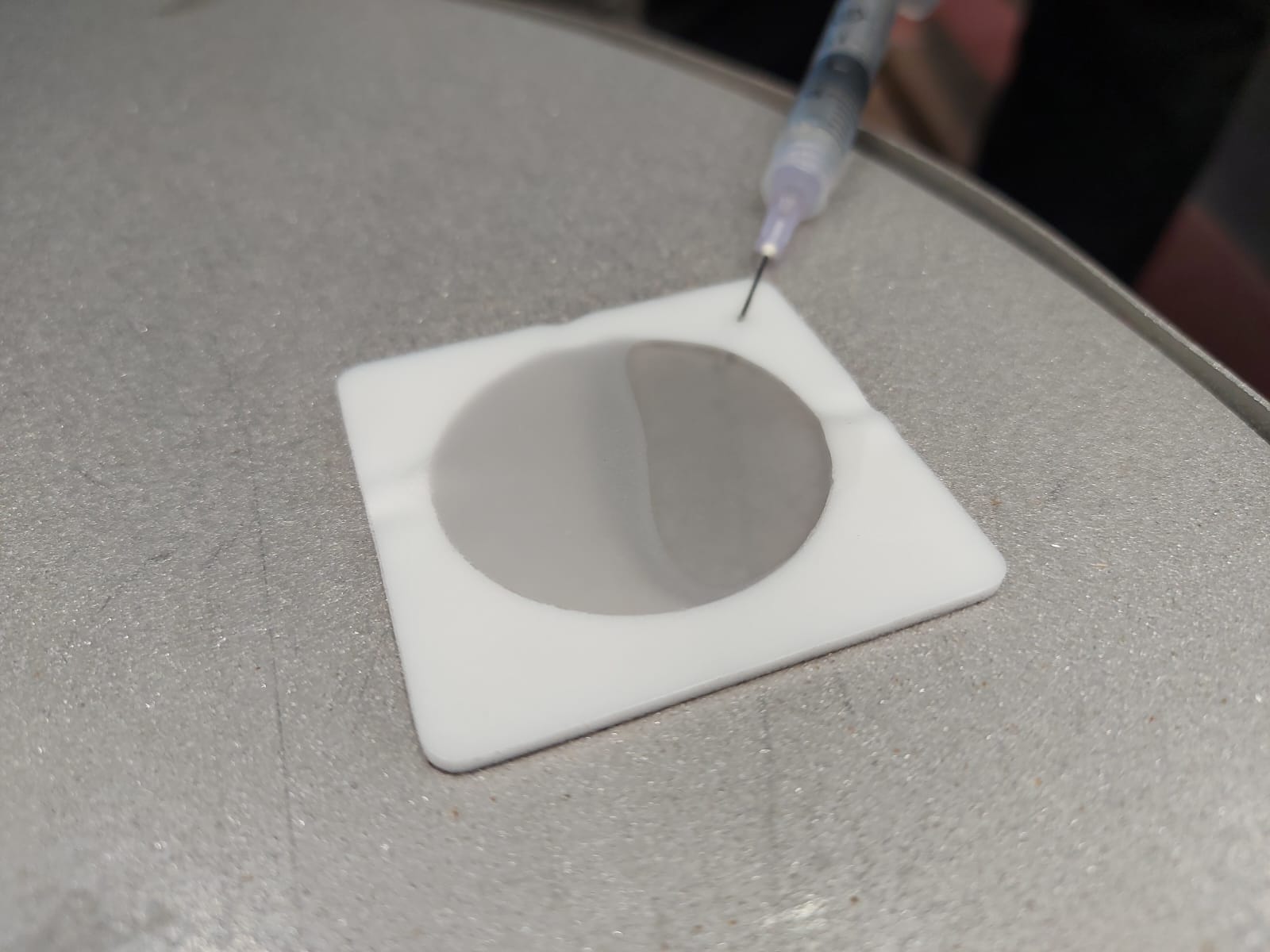
Bresle Test: The Bresle test involves placing a pre-measured volume of distilled water onto the blasted surface. After shaking the solution, a sample is taken and tested for conductivity, indicating the presence of soluble salts.
Stepwise Understanding: Sample Collection: Extract a representative sample from the solution for accurate testing.
Conductivity Measurement: Measure the conductivity of the sample using the conductivity meter.
Salt Calculation: Calculate the salt contamination level using the established correlation between conductivity and salt concentration.
Measurement Unit Calculation and Chart Understanding:
Salt contamination is typically expressed in micrograms of salt (NaCl) per square centimeter (µg/cm²). The relationship between conductivity and salt concentration is often linear, allowing for direct conversion of conductivity readings to salt values. Charts and graphs can visually represent this correlation.
| Conductivity μS/cm | Conductivity mS/m | As chloride μg/cm2 | As chloride mg/m2 | As sodium chloride μg/cm2 | As sodium chloride mg/m2 | As mixed salts μg/cm2 | As mixed salts mg/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 | 0.36 | 3.6 | 0.6 | 6 | 0.5 | 5 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 18 | 3 | 30 | 2.5 | 25 |
| 10 | 1 | 3.6 | 36 | 6 | 60 | 5 | 50 |
| 20 | 2 | 7.2 | 72 | 12 | 120 | 10 | 100 |
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bresle_method
Results and Interpretation:
Interpret the conductivity readings to determine the salt value on the blasted surface. Compare the obtained salt value to industry standards or project specifications to assess whether the surface meets acceptable levels of salt contamination. High salt values may indicate the need for further surface preparation before coating application.
Acceptance Criteria:
The acceptance criteria for salt contamination can vary based on industry standards, coating type, and environmental conditions. Commonly accepted salt values are often specified by coating manufacturers, project specifications, or relevant standards like ISO 8502-6.
Conclusion:
The salt contamination test on blasted surfaces is a crucial step in ensuring the long-term performance of coatings. Proper surface preparation and salt value assessment prevent coating failures due to poor adhesion and corrosion. By following a systematic process, utilizing accurate measurement units, and adhering to appropriate acceptance criteria, industries can achieve optimal coating protection and durability on their surfaces.
Hashtag:
#CoatingProtectionInsights
#Saltcontaminationinblasting
#blastinginspection
References:
ISO 8502-6: Preparation of steel substrates before application of paints and related products - Tests for the assessment of surface cleanliness - Part 6: Extraction of soluble contaminants for analysis – The Bresle Method
ASTM D4940: Standard Test Method for Conductimetric Analysis of Water Soluble Ionic Contamination of Blasting Abrasives
NACE International: Surface Preparation of Steel and Other Hard Materials by Water Jetting Prior to Coating Application
SSPC: The Society for Protective Coatings - Technical Resources
Published papers from corrosion and coating-related journals
Furthermore details,
Contact Us, BG Group of Paint and Coating Consultant
Contact Us: Whatsapp
Email : support@bgcoating.com






